Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and managing it effectively is crucial to maintaining a good quality of life. Whether you’ve just been diagnosed with diabetes or have been living with it for years, understanding how to manage the condition can help prevent complications and ensure long-term health. At Brobbson Pharmacy, we’re here to support you every step of the way. This comprehensive guide covers essential aspects of diabetes management, from medications to lifestyle changes.
Understanding Diabetes
Diabetes occurs when your body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or can’t effectively use the insulin it does produce. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar (glucose) levels. Without proper management, diabetes can lead to high blood sugar levels, which can cause serious health issues, including heart disease, nerve damage, kidney failure, and vision problems.
Types of Diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the body attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. People with Type 1 diabetes require insulin therapy.
- Type 2 Diabetes: The most common form, where the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin. It can often be managed with lifestyle changes, oral medications, and sometimes insulin.
- Gestational Diabetes: Occurs during pregnancy and usually goes away after childbirth, but it increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
Medication Management
For many people with diabetes, medications are an essential part of managing blood sugar levels. Whether you’re on oral medications, insulin, or other injectable therapies, it’s important to take your medications as prescribed and to understand how they work.
1. Insulin Therapy:
- Types of Insulin: There are different types of insulin, including rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting insulin. Your healthcare provider will prescribe the type of insulin that best meets your needs.
- Administration: Insulin can be administered using syringes, insulin pens, or insulin pumps. It’s important to rotate injection sites to prevent skin complications.
- Storage: Insulin should be stored in the refrigerator before it’s opened. After opening, it can be kept at room temperature for a certain period, depending on the type of insulin.
2. Oral Medications:
- Metformin: Often the first medication prescribed for Type 2 diabetes, it works by reducing glucose production in the liver and improving insulin sensitivity.
- Sulfonylureas: These medications help your body produce more insulin.
- DPP-4 Inhibitors: They help reduce blood sugar levels without causing hypoglycemia.
- SGLT2 Inhibitors: These medications help the kidneys remove glucose from the bloodstream.
3. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists:
- Injectable Medications: These drugs help regulate blood sugar by enhancing insulin production, slowing digestion, and reducing appetite.
Medication Adherence:
- Stick to Your Schedule: It’s crucial to take your medications at the same time every day. Use pill organizers, alarms, or mobile apps to help you remember.
- Monitor Side Effects: Report any side effects to your healthcare provider. Common side effects might include gastrointestinal issues with metformin or hypoglycemia with insulin or sulfonylureas.
- Consult Your Pharmacist: At Brobbson Pharmacy, our pharmacists are available to discuss your medications, answer any questions, and help you manage side effects.
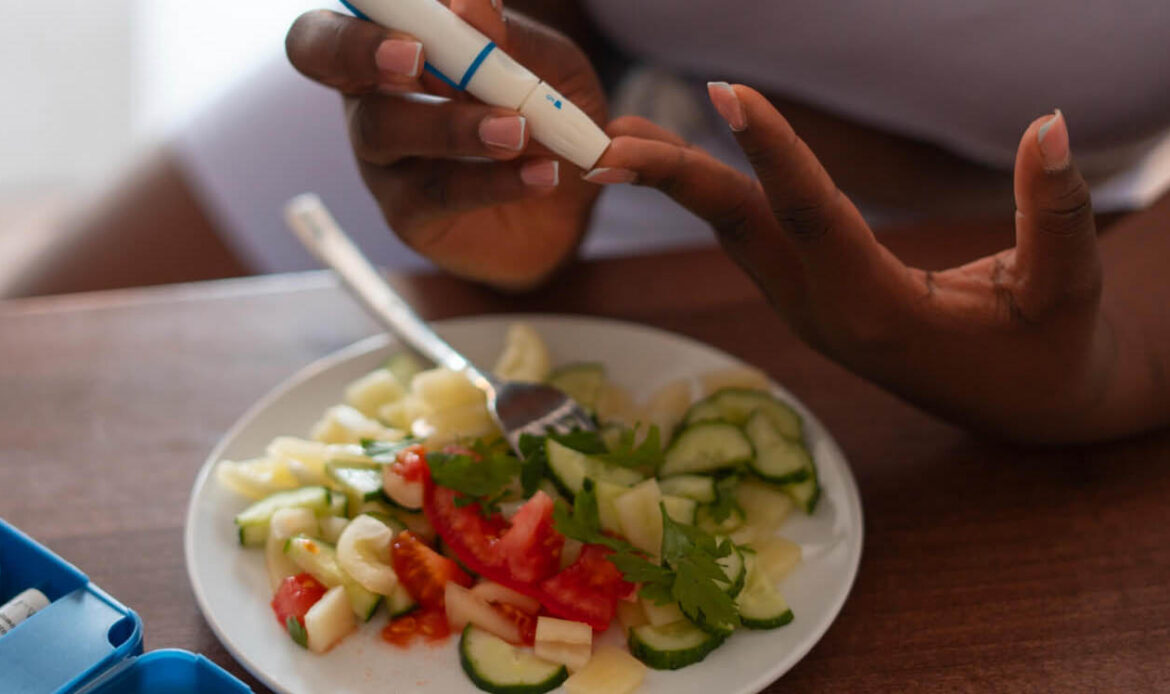
Blood Sugar Monitoring
Regular monitoring of your blood sugar levels is a key component of diabetes management. It helps you understand how your body responds to food, exercise, medications, and other factors.
1. Blood Glucose Meters:
- Choosing the Right Meter: There are various types of blood glucose meters available, from basic models to more advanced ones with Bluetooth connectivity. Choose one that suits your needs and lifestyle.
- How to Test: Prick your fingertip with a lancet, place a drop of blood on a test strip, and insert it into the meter. The meter will display your blood sugar level within seconds.
- Tracking Your Results: Keep a log of your blood sugar levels to share with your healthcare provider. Many meters can store readings or sync with mobile apps for easy tracking.
2. Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM):
- How It Works: A CGM system uses a small sensor placed under the skin to monitor blood glucose levels continuously throughout the day and night. The sensor transmits data to a device or smartphone, providing real-time glucose readings.
- Benefits: CGMs provide a more comprehensive picture of your blood sugar levels and can alert you to highs and lows before they become dangerous.
3. A1C Testing:
- What It Measures: The A1C test provides an average blood sugar level over the past two to three months. It’s a key indicator of how well your diabetes is being managed.
- Target Levels: Most people with diabetes should aim for an A1C level of below 7%, but your target may vary based on individual factors.
Healthy Eating
Diet plays a vital role in managing diabetes. What you eat can have a direct impact on your blood sugar levels, so it’s important to make informed food choices.
1. Understanding Carbohydrates:
- Carb Counting: Carbohydrates have the most significant effect on blood sugar levels. Learn to count carbs to better manage your intake and control your blood sugar.
- Glycemic Index: Choose foods with a low glycemic index (GI), as they cause a slower rise in blood sugar levels compared to high-GI foods.
2. Balanced Meals:
- Portion Control: Use portion control to avoid overeating and to manage your weight, which is crucial for controlling blood sugar levels.
- Include Fiber: High-fiber foods, such as vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, help slow the absorption of sugar and improve blood sugar control.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporate healthy fats, like those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil, into your diet. These fats can help you feel fuller and more satisfied, reducing the temptation to overeat.
3. Meal Planning:
- Plan Ahead: Planning your meals in advance can help you make healthier food choices and avoid last-minute, high-sugar options.
- Consult a Dietitian: A registered dietitian can help create a personalized meal plan that fits your lifestyle, preferences, and blood sugar management goals.
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is beneficial for everyone, but it’s especially important for people with diabetes. Exercise helps lower blood sugar levels, improves insulin sensitivity, and supports overall health.
1. Types of Exercise:
- Aerobic Exercise: Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling help improve cardiovascular health and burn calories.
- Strength Training: Building muscle mass through strength training exercises like weightlifting or resistance bands can help your body use insulin more effectively.
- Flexibility and Balance: Yoga and stretching exercises improve flexibility, balance, and relaxation, which are all important aspects of overall fitness.
2. Exercise Safety:
- Check Blood Sugar Levels: Monitor your blood sugar before, during, and after exercise to avoid hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water before, during, and after exercise to stay hydrated.
- Wear Proper Footwear: Choose supportive shoes to prevent foot injuries, which can be more serious for people with diabetes.
3. Setting Realistic Goals:
- Start Slowly: If you’re new to exercise, start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts.
- Consistency is Key: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Consistency is more important than intensity.
Managing Stress
Stress can have a significant impact on blood sugar levels, making it harder to manage diabetes. It’s important to find ways to reduce and manage stress in your life.
1. Mindfulness and Relaxation:
- Practice Mindfulness: Mindfulness meditation and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress and improve focus.
- Engage in Relaxing Activities: Activities like reading, listening to music, or spending time in nature can help you relax and lower stress levels.
2. Time Management:
- Prioritize Tasks: Managing your time effectively can reduce stress. Focus on what’s most important and delegate tasks when possible.
- Set Boundaries: Learn to say no to avoid overcommitting and becoming overwhelmed.
3. Seek Support:
- Talk to Someone: Whether it’s a friend, family member, or therapist, talking about your stress can help you feel more supported and less isolated.
- Join a Support Group: Connecting with others who are managing diabetes can provide valuable insights, encouragement, and support.
Brobbson Pharmacy’s Support Services
At Brobbson Pharmacy, we understand the challenges of managing diabetes and are here to support you every step of the way. Our services are designed to make diabetes management easier and more effective.
Our Services Include:
- Medication Therapy Management (MTM): Our pharmacists provide personalized reviews of your medications to ensure they are working effectively and safely.
- Blood Glucose Monitoring Supplies: We offer a wide range of glucose meters, test strips, and lancets to help you monitor your blood sugar levels.
- Diabetes Education: Our pharmacists are available to provide education on diabetes management, including how to use insulin, carb counting, and more.
- Nutritional Counseling: We can help you create a diet plan that supports your blood sugar control and overall health.
- Immunizations: People with diabetes are at higher risk for certain infections, so we offer vaccines like the flu shot and pneumonia vaccine to help protect your health.
Take charge of your diabetes management today. Visit Brobbson Pharmacy for personalized support and services, or Contact Us to schedule a consultation with one of our expert pharmacists.